When it comes to powering network devices, Power over Ethernet (PoE) technology has revolutionized the way we set up and manage our networks. Two essential components of PoE systems are PoE injectors and PoE switches. While both devices serve the purpose of delivering power and data over a single Ethernet cable, they have distinct differences that make them suitable for various applications. In this article, we’ll dive deep into the world of PoE injectors and PoE switches, exploring their working principles, key features, and the scenarios where each device shines. By the end of this comprehensive comparison, you’ll have a clear understanding of when to use a PoE injector vs PoE switch to optimize your network’s performance and efficiency.
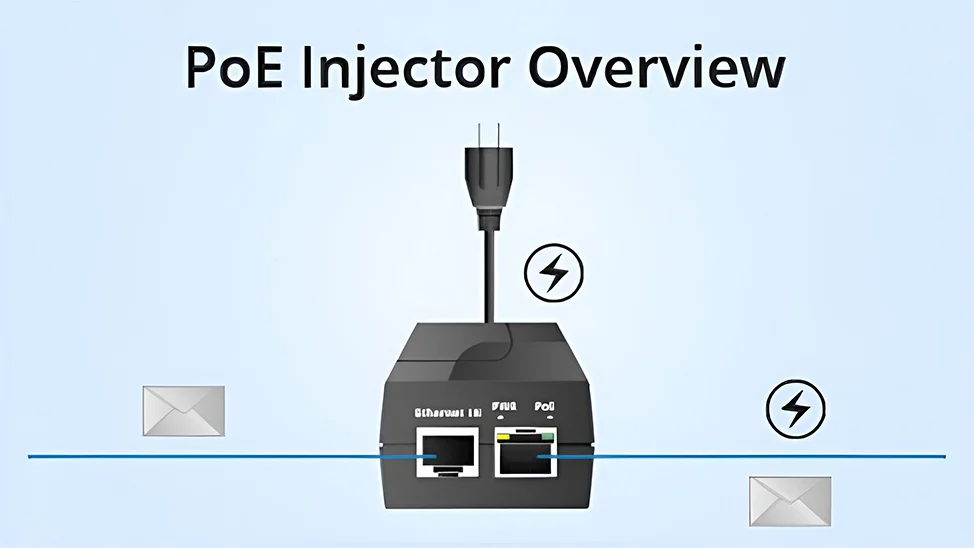
What is a PoE injector?
A PoE injector is a compact device that adds Power over Ethernet functionality to non-PoE devices or network segments. It works by combining power from an external power supply with the data signal from a non-PoE switch or router, and then transmitting both power and data over a single Ethernet cable to the connected device. PoE injectors offer a cost-effective solution for powering a small number of PoE devices, such as IP cameras, VoIP phones, or wireless access points, without the need to replace existing non-PoE network infrastructure.
Key features and benefits of PoE injectors include:
Flexibility: PoE injectors allow you to add PoE functionality to specific devices or network segments without upgrading your entire network.
Cost-effectiveness: For small-scale deployments, PoE injectors are often more affordable than purchasing a PoE switch.
Easy installation: PoE injectors are plug-and-play devices that require minimal configuration, making them easy to set up and deploy.
PoE injectors are available in various types, including single-port, multi-port, and gigabit models, catering to different network requirements and device compatibilities.
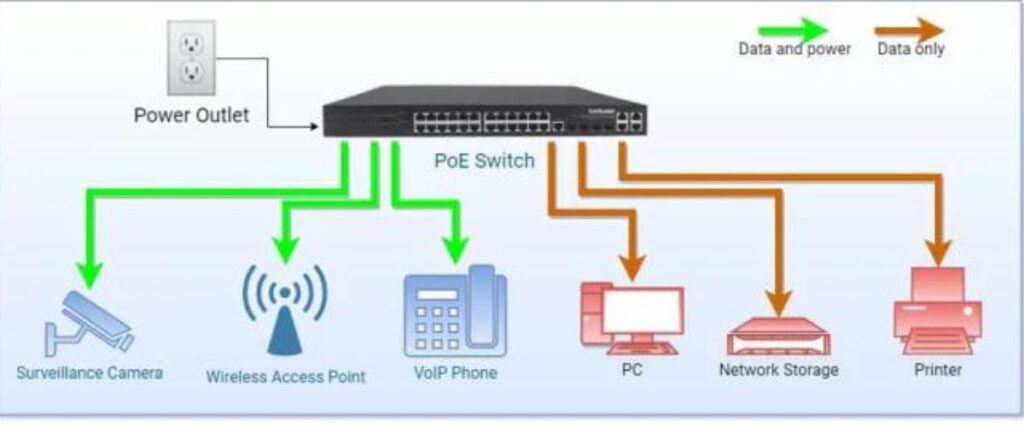
What is a PoE Switch?
A PoE switch is an Ethernet switch that has built-in Power over Ethernet functionality, allowing it to deliver both power and data to multiple PoE-enabled devices through a single cable. PoE switches are designed to simplify network setup and management by eliminating the need for separate power cables and outlets for each connected device. They are ideal for larger networks or environments where multiple PoE devices need to be powered and managed centrally.
Key features and benefits of PoE switches include:
Scalability: PoE switches offer a scalable solution for powering multiple PoE devices, making them suitable for growing networks.
Centralized management: PoE switches allow for easy monitoring and control of connected devices through a single interface.
Advanced features: Many PoE switches come with additional features, such as VLAN support, QoS, and remote management, enhancing network performance and security.
PoE switches come in various types, including unmanaged, smart, and managed models, catering to different network sizes, complexities, and management requirements.

PoE Injector vs PoE Switch: Key Differences
When comparing PoE injectors and PoE switches, several key differences emerge:
Power capacity and scalability: PoE switches typically offer higher power budgets and can support a larger number of PoE devices compared to PoE injectors.
Cost and cost-effectiveness: While PoE injectors are more affordable for small-scale deployments, PoE switches become more cost-effective as the number of connected devices increases.
Flexibility and ease of installation: PoE injectors offer greater flexibility for adding PoE functionality to specific devices or network segments, while PoE switches provide a more streamlined installation process for larger networks.
Network management and control: PoE switches offer centralized management and advanced features for monitoring and controlling connected devices, whereas PoE injectors have limited management capabilities.
Security and reliability: PoE switches often include built-in security features and redundancy options, ensuring a more robust and secure network infrastructure compared to PoE injectors.
Power consumption and efficiency: PoE switches are generally more power-efficient than PoE injectors, as they optimize power allocation and minimize power loss across the network.
When to Use a PoE Injector
PoE injectors are the preferred choice in the following scenarios: Small-scale deployments: When you need to power a limited number of PoE devices, such as a single IP camera or a few VoIP phones, a PoE injector is a cost-effective solution.
Retrofitting existing networks: If you want to add PoE functionality to a non-PoE network without replacing the existing switches or routers, PoE injectors allow you to do so easily.
Temporary or remote installations: PoE injectors are ideal for temporary setups or remote locations where a full PoE switch may not be necessary or practical.
However, it’s essential to consider the limitations of PoE injectors, such as their limited power capacity, lack of advanced management features, and potential for increased clutter due to the need for additional power adapters.
When to Use a PoE Switch
PoE switches are the preferred choice in the following scenarios:
Large-scale deployments: When you need to power and manage a significant number of PoE devices, a PoE switch offers a scalable and efficient solution.
Centralized management: If you require advanced monitoring, control, and configuration of your PoE devices, a PoE switch with management capabilities is the way to go.
Future-proofing your network: PoE switches provide a foundation for future growth and expansion, allowing you to easily add more PoE devices as your network evolves.
However, PoE switches also have their limitations, such as higher upfront costs compared to PoE injectors and the potential for over-provisioning power capacity in smaller networks.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Between PoE Injector and PoE Switch
When deciding between a PoE injector and a PoE switch, consider the following factors:
Network size and scalability requirements: Assess your current network size and anticipate future growth to determine which solution best fits your needs.
Budget and cost constraints: Evaluate the upfront and long-term costs associated with each option, taking into account the number of devices you need to power.
Existing network infrastructure: Consider your current network setup and whether you need to retrofit PoE functionality or build a new PoE-enabled network from scratch.
Future expansion plans: Think about your long-term network goals and choose a solution that can accommodate your future needs.
Specific application needs: Assess the power requirements and management features needed for your specific applications, such as IP cameras, VoIP phones, or wireless access points.
Power requirements of connected devices: Ensure that the chosen solution can provide sufficient power to all connected devices, taking into account their individual power consumption and the total power budget of the PoE injector or switch.
PoE Injector and PoE Switch Setup and Configuration
Setting up a PoE injector or PoE switch is generally straightforward, but there are some best practices to follow for optimal performance:
For PoE injectors:
Connect the PoE injector to a power outlet and the non-PoE switch or router using Ethernet cables.
Connect the PoE device to the PoE injector using an Ethernet cable.
Ensure that the PoE injector is compatible with the power requirements of the connected device.
For PoE switches:
Connect the PoE switch to a power outlet and your network infrastructure using Ethernet cables.
Configure the PoE switch using the management interface, setting up VLANs, QoS, and other advanced features as needed.
Connect your PoE devices to the PoE switch using Ethernet cables, ensuring that the switch has sufficient power budget to support all connected devices.
Troubleshooting Common PoE Issues
When encountering issues with your PoE setup, consider the following:
Power-related problems: Ensure that the PoE injector or switch is providing sufficient power to the connected devices and that the devices are compatible with the PoE standard being used.
Compatibility issues: Verify that the PoE devices and the PoE injector or switch are compatible with each other and support the same PoE standards.
Network connectivity and performance: Check for proper cable connections, network configuration, and bandwidth availability to ensure optimal performance.
Future of PoE Technology
As PoE technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see the following advancements:
Higher power capacity: The IEEE 802.3bt standard, also known as PoE++, allows for up to 90W of power per port, enabling the connection of more power-hungry devices.
Increased efficiency: Improvements in PoE technology will lead to more efficient power delivery and reduced power loss, lowering overall energy consumption.
Smarter management: The integration of AI and machine learning will enable more intelligent power allocation, automated troubleshooting, and predictive maintenance for PoE networks.
These advancements may influence the choice between PoE injectors and PoE switches in the future, as higher power capacities and smarter management features become more widely available.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the differences between PoE injectors and PoE switches is crucial for making informed decisions when setting up or expanding your network. PoE injectors offer a cost-effective and flexible solution for small-scale deployments or retrofitting existing networks, while PoE switches provide scalability, centralized management, and advanced features for larger networks. By assessing your specific network requirements, budget, and future growth plans, you can choose the right PoE solution to optimize your network’s performance and efficiency. As PoE technology continues to evolve, staying informed about the latest advancements and their potential impact on your network will help you make the best decisions for your organization’s needs.